Faculty Contact Info
POSTDOCTORAL, LAB TECHNICIAN & PREDOCTORAL STUDENT POSITIONS CURRENTLY AVAILABLE
Please send CVs to yuruliu@uic.edu
Yuru Liu, PhD
ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR OF PHARMACOLOGY
B.M. Nanjing University; Medicine (1993).
Ph.D. Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine; Developmental Genetics (2000).
Postdoc, Duke University & Vanderbilt University; Developmental Biology of Lung (2004).
Postdoc, University of Chicago; Developmental Biology of Lung (2007).
Research Interests
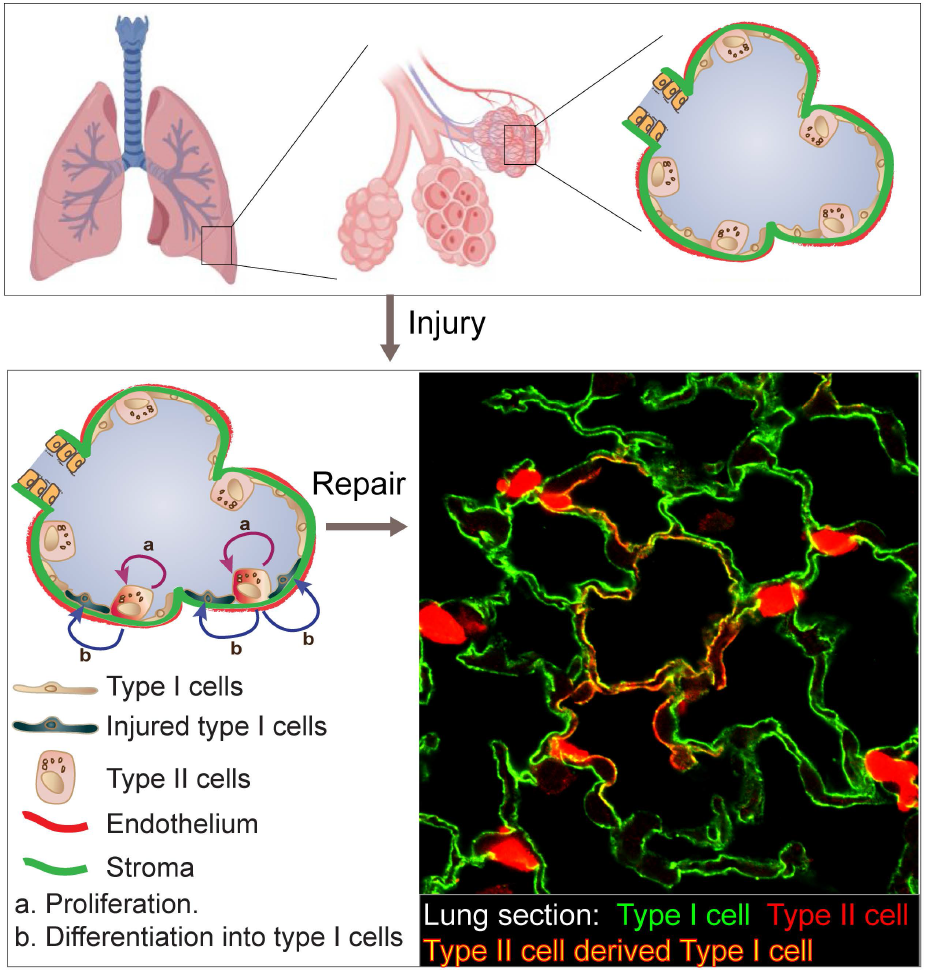
The normal alveolar epithelium is composed of two types of cells: flat type I cells, which comprise 95% of the gas-exchange surface, and cuboidal type II cells that secrete pulmonary surfactant. Injury of alveoli activates programs in potent type II cells that result in proliferation and differentiation into type I cells leading to alveolar barrier repair. Thus, type II cells function as “facultative stem cells” that have a crucial role in repair of the alveolar surface. We use mouse lung injury models to define sub-population of type II cells for the progenitor cell function. We also use genetic models to define the proteins responsible for transition of type II cells to type I cells required for recovery from alveolar injury. We are currently focusing on three areas: 1) The factors that induce the progenitor cells phenotype of type II cell. 2)The interactions of type II cells with surrounding stem cell niche. 3)The consequences of functionally disrupting activated type II cells in the mechanism of chronic lung diseases.

Selected Publications
Chan M and Liu Y. Function of epithelial stem cell in the repair of alveolar injury. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022 Apr 27;13(1):170. doi: 10.1186/s13287-022-02847-7.
Chen Q, Rehman J, Chan M, Fu P, Dudek SM, Natarajan V, Malik AB and Liu Y. Angiocrine sphingosine-1-phosphate activation of S1PR2-YAP signaling axis in alveolar type II cells is essential for lung repair Cell Reports, 2020. 31(13):107828. PMCID: PMC7371431
Chen Q, Liu Y. Heterogeneous groups of alveolar type II cells in lung homeostasis and repair. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2020 Dec 1;319(6):C991-C996. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00341.2020.
Finn J, Sottoriva K, Pajcini KV, Kitajewski JK, Chen C, Zhang W, Malik AB and Liu Y. Dlk1-Mediated Temporal Regulation of Notch Signaling is Required
for Differentiation of Alveolar Type II to Type I Cells During Lung Repair. Cell Reports, 2019, Mar 12;26(11):2942-2954.
Ebenezer DL, Berdyshev EV, Bronova IA, Liu Y, Tiruppathi C, Komarova Y, Benevolenskaya EV, Suryadevara V, Ha AW, Harijith A, Tuder RM, Natarajan V, Fu P. Pseudomonas aeruginosa stimulates nuclear sphingosine-1-phosphate generation and epigenetic regulation of lung inflammatory injury. Thorax, 2019, Feb 5. pii: thoraxjnl-2018-212378. doi: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2018-212378. [Epub ahead of print]
Chen Q, Suresh Kumar V, Finn J, Jiang D, Liang J, Zhao YY, Liu Y. CD44-high alveolar type II cells show stem cell properties during steady-state alveolar homeostasis. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2017 Jul 1;313(1): L41-L51. PMCID:PMC5538873
Liu Y. "Chapter 2: Type II Cells as Progenitors in Alveolar Repair" in "Lung Stem Cells in Epithelium and Vasculature", Jason Yuan and Amy Firth Ed., (Springer, New York, 2015), pp 13-33.
Chignalia AZ, Vogel SM, Reynolds AB, Mehta D, Dull RO, Minshall RD, Malik AB, Liu Y. p120-catenin expressed in alveolar type II cells is essential for the regulation of lung innate immune response. Am J Path. 185:1251-63, 2015.
Chernaya O, Shinin V, Liu Y, Minshall RD. Behavioral Heteogeneity of Adult Mouse Lung Epithelial Progenitor Cells. Stem Cells Dev. 23:2744-57, 2014.
Liu Y, Suresh Kumar V, Zhang W, Rehman J, Malik AB. Activation of Type II Cells into Regenerative Sca-1+ Cells During Alveolar Repair. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. Dec 3, 2014 [Epub ahead of print]
Liu Y, Sadikot RT, Adami GR, Kalinichenko VV, Pendyala S, Natarajan V, Zhao YY, Malik AB. FoxM1 mediates the progenitor function of type II epithelial cells in repairing alveolar injury induced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Exp Med. 208:1473-84, 2011.

